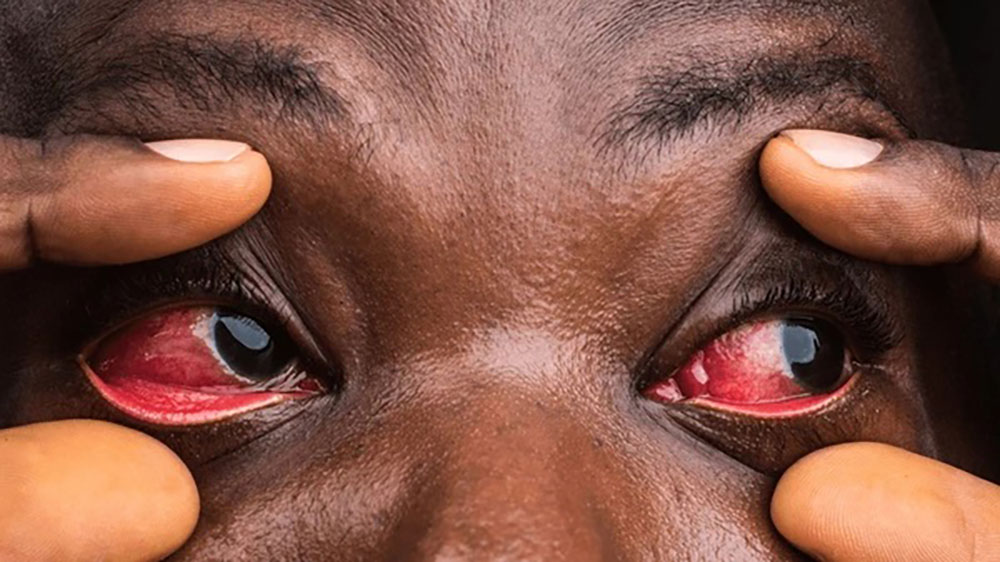
Recently, cases of red eyes/conjunctivitis have been on the rise. But are you familiar with the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods? In this article, we will explore the common causes, symptoms, and how to prevent the spread of this viral disease.
What is Conjunctivitis / Red Eye ?
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin, transparent layer of tissue that lines the inner surface of the eyelid and covers the white part of the eye. When the blood vessels in this tissue become inflamed, they dilate, giving the eye a reddish or pinkish appearance.
Causes of Conjunctivitis / Red Eye:
- Viral Infections: Viral conjunctivitis is highly contagious and is often associated with the same viruses that cause the common cold. It spreads easily through direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces.
- Bacterial Infections: Bacterial conjunctivitis is typically caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pneumoniae. It can also spread through direct contact or by touching contaminated objects.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergic conjunctivitis occurs when the eye comes into contact with allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain chemicals. It is not contagious but can be triggered by environmental factors or specific allergens.
- Environmental Irritants: Exposure to smoke, pollution, chemicals, or other irritants can lead to irritation and redness of the eyes, resembling conjunctivitis symptoms.
Symptoms of Conjunctivitis / Red Eye:
- Redness in the white of the eye or inner eyelid
- Watery or thick discharge from the eye, which may be clear, yellow, or green
- Itchiness or irritation in the affected eye(s)
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Sensitivity to light
- Crusting of eyelids or lashes, especially in the morning
Treatment Options for Conjunctivitis / Red Eye:
- Viral Conjunctivitis: Since viral conjunctivitis is caused by a virus, antibiotics are ineffective. Treatment typically involves supportive care such as applying warm compresses to soothe discomfort, using over-the-counter artificial tears to alleviate dryness, and practicing good hygiene to prevent spreading the infection. Symptoms usually resolve on their own within one to two weeks.
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Bacterial conjunctivitis may require antibiotic eye drops or ointments prescribed by a healthcare professional. It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as directed, even if symptoms improve sooner. Warm compresses can also help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: Avoiding allergens whenever possible is the primary strategy for managing allergic conjunctivitis. Over-the-counter antihistamine eye drops or oral medications can help alleviate symptoms. Cold compresses may provide relief from itchiness and swelling.
- Environmental Irritants: Minimizing exposure to irritants such as smoke, dust, and chemicals can prevent or reduce symptoms of conjunctivitis. Wearing protective eyewear in dusty or hazardous environments can also help.
Prevention Tips:
- Wash/ sanitize your hands frequently.
- Avoid rubbing or touching the eyes unnecessarily.
- Practice good hygiene, including regularly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces and objects that come into contact with the eyes.
- Avoid sharing towels, pillows, or other personal items with individuals who have conjunctivitis.
Conclusion:
Conjunctivitis / Red Eye is a common eye condition that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, allergies, or environmental irritants. While it can be uncomfortable and inconvenient, most cases of conjunctivitis resolve on their own or with appropriate treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for conjunctivitis is crucial for effectively managing the condition and preventing its spread.
If you experience persistent or severe symptoms of conjunctivitis, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.